Unearned Revenue Definition
As a result of this prepayment, the seller has a liability equal to the revenue earned until the good or service is delivered. Unearned revenue is capital received for services not yet rendered. It assumes a variety of forms, from rent paid in advance to contracts made before the delivery of services. For instance, assume your company rents office space and pays its landlord $50,000 in December for rent covering the period of January through May.
The company receives an Annual subscription of Rs from one of its clients on 31.03.2018 for the next year. Revenue will be earned when the magazine will be delivered to the client on a monthly basis. Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2018 will show an increase in Cash Balance by the amount of Annual subscription of Rs and Unearned Income, a liability, will be created.
There are many services a business might provide that generate unearned revenue, such as a cleaning service. Using this as an example, unearned revenue is recorded if the buyer has purchased the cleaning service but not yet received it. An unearned revenue adjusting entry reflects a change to a previously stated amount of unearned revenue. Unearned revenue is any amount that a customer pays a business in advance.
Permanent – balance sheet accounts including assets, liabilities, and most equity accounts. So, the ending balance of this period will be the beginning balance for next period. Unearned sales is largest in the January quarter where most of the large enterprise accounts buy their subscription services.
The single major difference between revenue (an income statement item) and assets (balance sheet items) is that revenue is recorded over the course of a period. For instance, Wal-Mart’s fourth-quarter revenue will reflect everything it sold from Oct. 1 to Dec. 31. This journal entry reflects the fact that the business has an influx of cash but that cash has been earned on credit. It is a pre-payment on goods to be delivered or services provided. Unearned revenue is originally entered in the books as a debit to the cash account and a credit to the unearned revenue account.
The cost of deferred revenue
If the company fails to deliver the promised product or service or a customer cancels the order, the company will owe the money paid by the customer. This is also a violation of the matching principle, since revenues are being recognized at once, while related expenses are not being recognized until later periods. As a company earns the revenue, it reduces the balance in the unearned revenue account (with a debit) and increases the balance in the revenue account (with a credit). The unearned revenue account is usually classified as a current liability on the balance sheet. Unearned revenue is money received from a customer for work that has not yet been performed.
Presumably, the buyer can defer the income recognition if it uses the accrual method. This result would force the buyer to recognize income for the deemed payment by making a credit to revenue and an offsetting debit entry to goodwill, because the seller paid no actual cash.15 This results in increasing the buyer’s purchase price. Accrued revenue is revenue https://www.bookstime.com/ that has been earned by providing a good or service, but for which no cash has been received. Accrued revenues are recorded as receivables on the balance sheet to reflect the amount of money that customers owe the business for the goods or services they purchased. Businesses sometimes need to make an unearned revenue adjusting entry to their balance sheet.
It should be noted that companies that use cash accounting still track accounts receivable – outstanding bills to customers. They just can’t record the revenue and put it on the balance sheet until bills are paid. Unearned revenue accounts for money prepaid by a customer for goods or services that have not been delivered.
It is critical to properly define the language in purchase agreements dealing with the tax treatment of deferred revenue accounts to help avoid surprises after closing, whether the adviser represents the buyer or the seller in an M&A transaction. The treatment of unearned revenue can have a material impact not only on taxes, revenue recognized by the seller, and revenue recognized by the buyer, but also on the amount of the working capital target in M&A transactions. Buyers and sellers would be wise to work together and bring more certainty to their intended tax treatment for unearned revenue for purposes of both tax and target working capital. FreshBooks has online accounting software for small businesses that makes it easy to generate balance sheets and view your unearned revenue.
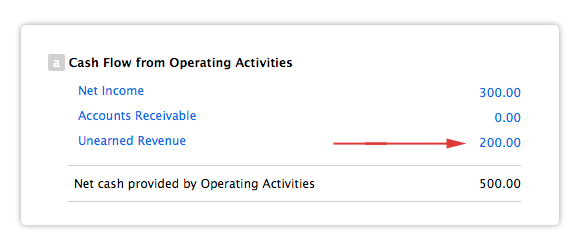
When the goods or services are provided, an adjusting entry is made. Unearned revenue is helpful to cash flow, according to Accounting Coach. The accrued revenue and accounts receivable entries in accrual accounting allow the company to recognize revenue and place it on the balance sheet as it earns the money.
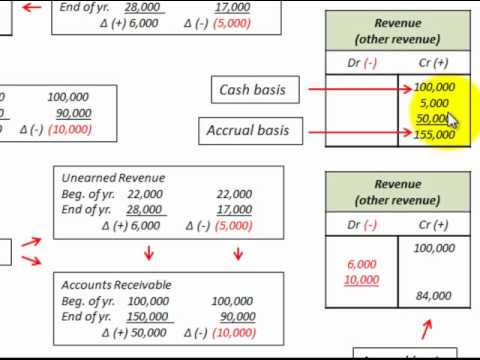
- If it is a monthly publication, as each periodical is delivered, the liability or unearned revenue is reduced by $100 ($1,200 divided by 12 months) while revenue is increased by the same amount.
- Image from AmazonBalance Sheet – Check out CFI’s Advanced Financial Modeling & Valuation Course for an in-depth valuation of Amazon.
- An unearned revenue adjusting entry reflects a change to a previously stated amount of unearned revenue.
- The first journal entry would reflect that $1,000 was paid, forming the company’s $1,000 worth of debit, or the total amount of money paid to the business but not yet earned.
- Permanent – balance sheet accounts including assets, liabilities, and most equity accounts.
- Temporary – revenues, expenses, dividends (or withdrawals) account.
There are variations of profit on the income statement that are used to analyze the performance of a company. More journal entries would then be entered for each of the next five months. Because $1,000 was paid and work will be done evenly throughout each month, the business would record a $200 debit to unearned revenue in each of the next five months. So, journal entries include not only an entry reflecting the total amount of unearned revenue but individual entries that break down the amount provided each month. The journal entry would reflect both the total amount paid and how that amount will be earned over time.
Unearned revenue is listed under “current liabilities.” It is part of the total current liabilities as well as total liabilities. At the end of the month, the owner debits unearned revenue $400 and credits revenue $400. how to record unearned revenue He does so until the three months is up and he’s accounted for the entire $1200 in income both collected and earned out. The business owner enters $1200 as a debit to cash and $1200 as a credit to unearned revenue.
Unearned revenue can provide clues into future revenue, although investors should note the balance change could be due to a change in the business. Morningstar increased quarterly and monthly invoices but is less reliant on up-front payments https://www.bookstime.com/unearned-revenue from annual invoices, meaning the balance has been growing more slowly than in the past. Morningstar Inc. (MORN) offers a line of products and services for the financial industry, includingfinancial advisorsand asset managers.
If it is a monthly publication, as each periodical is delivered, the liability or unearned revenue is reduced by $100 ($1,200 divided by 12 months) while revenue is increased by the same amount. Unearned Sales results in cash exchange before revenue recognition for the business. However, if a business does not follow the correct accrual method of recognition of Deferred Revenue it can overstate the revenue and resultant profitability without recognizing the corresponding expenses to generate such revenue. Furthermore, that will also lead to a violation of the Matching Principle of unearned income accounting which requires that both expense and related income should be reported in the same period to which it belongs. Accrued revenue is recorded in the financial statements through the use of an adjusting journal entry.
Accrued Revenue Journal Entries

If a company requires prepayment for its goods, it would recognize the revenue as unearned, and would not recognize the revenue on its income statement until the period for which the goods or services were delivered. In accounting terms, unearned revenue forms a debit, or loss, to the recipient.
Temporary – revenues, expenses, dividends (or withdrawals) account. These account balances do not roll over into the next period after closing. The closing process reduces revenue, expense, and dividends account balances (temporary accounts) to zero so they are ready to receive data for the next accounting period. Under the accrual basis of accounting, revenues received in advance of being earned are reported as a liability. If they will be earned within one year, they should be listed as a current liability.
Stark contrasts exist between these types of capital; enough so that in a very basic way accrued revenue constitutes the opposite of unearned revenue. Accrued revenue—an asset on the balance sheet—is revenue that has been earned, but for which no cash has been received. An accountant records adjustments for accrued revenues through debit and credit journal entries in defined accounting periods to account for accrued revenues accurately and so that the balance sheetremains in balance.
For reporting purposes, a business must classify all items as either assets or liabilities. However, if a business receives a prepayment on an order, the prepayment is classified as a liability because the payment represents something that is not yet earned and is therefore owed to the customer. Upon delivery of the good or service to the customer, the deferred revenue is reclassified as an asset. Under this method when Deferred Revenue is received by the business, a liability account is created.
It ended up being 8 years for a number of reasons and about $80 dollars of every sale was considered online software. Expressed as a percentage, the net profit margin shows how much of each dollar collected by a company as revenue translates into profit. Operating profit is gross profit minus all other fixed and variable expenses associated with operating the business, such as rent, utilities, and payroll.

